
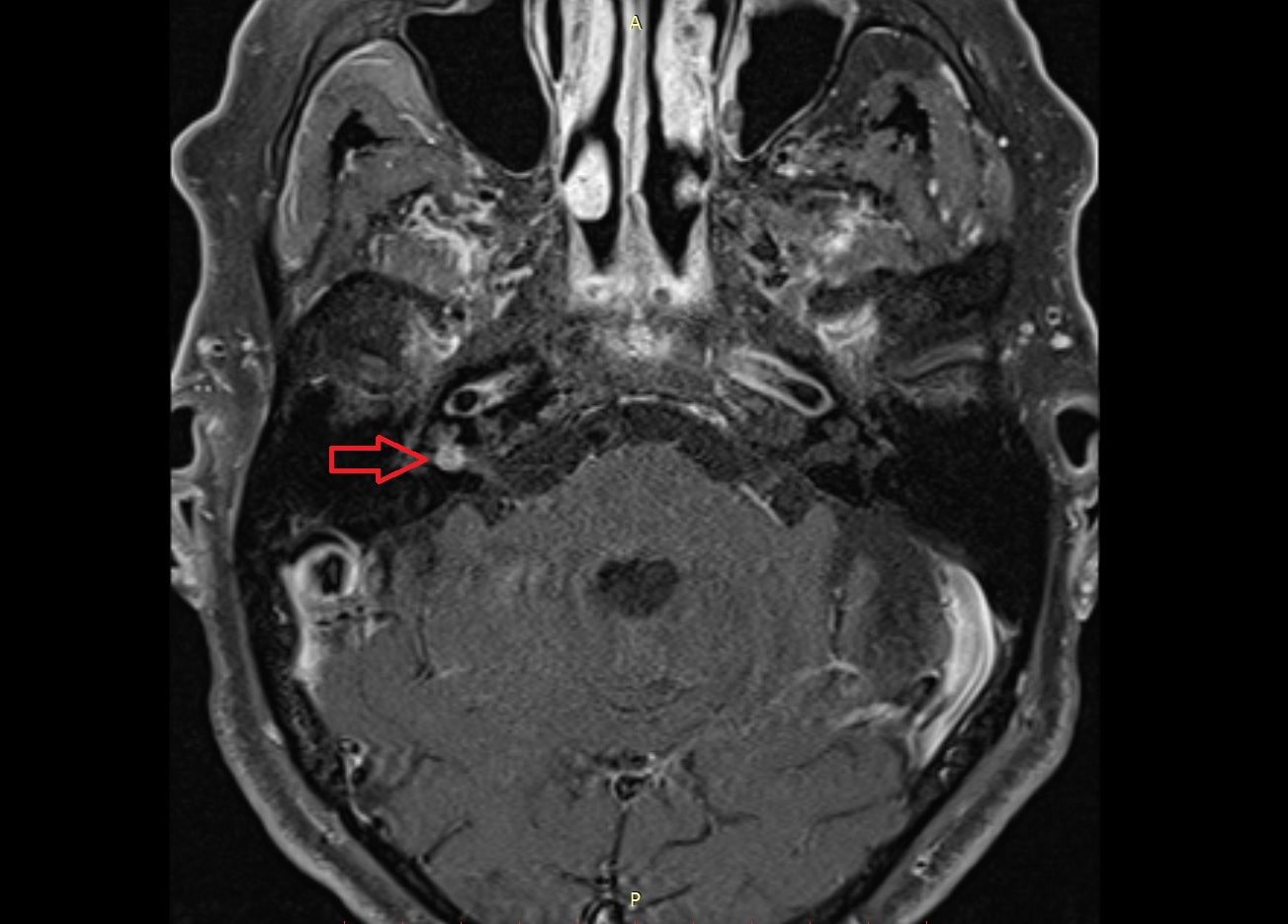
Additional anomalies need to be looked for as well, such as the presence of severe incudomallear dysplasia, which when present has to be resected, as well as dysplastic stapes, which may need to be replaced by a prosthesis. In addition, we also need to look for structures that may cause problems during surgery such as reduced volume of the middle ear cavity and poor pneumatization of the temporal bone. Preoperatively, the radiologist should look for contraindications for surgery such as atretic oval and or round window and unfavorable course of the facial nerve.

HRCT of the temporal bone is indicated for preoperative planning. The outcome of surgeries performed in the presence of middle and inner ear dysplasia are not encouraging. Isolated EAC atresias are amendable to surgery. She suffered from severe sensorineural hearing loss on the left side.Atresia of the EAC can occur in isolation or it may be associated with middle ear and inner ear dysplasia. On the left images of a woman who had fallen down from the stairs three days earlier. There is a subtle otosclerotic focus in the characteristic site: the fissula ante fenestram (arrows). On the left a transverse CT-image of a 23-year old female with conductive hearing loss. It can also occur around the cochlea (retrofenestral otosclerosis). in front of the oval window (fenestral otosclerosis). The process starts in the region of the oval window, classically at the fissula ante fenestram, i.e. However, involvement of other portions of the otic capsule can result in mixed sensorineural hearing loss.
When this process involves the oval window in the region of the footplate, the footplate becomes fixed, resulting in conductive hearing loss.Ĭonductive hearing loss develops early in the third decade and is considered to be the hallmark of the disease. It is sometimes called otospongiosis because the disease begins with an otospongiotic phase, which is followed by an otosclerotic phase when osteoclasts are replaced by osteoblasts and dense sclerotic bone is deposited in areas of previous bone resorption. Otosclerosis is a genetically mediated metabolic bone disease of unknown etiology. This favors the diagnosis of cholesteatoma. There were granulations on the left ear drum.ĬT demonstrates a soft tissue mass between the ossicular chain and the lateral tympanic wall, which is eroded. On the left a 20-year old woman with recurrent otitis. Large cholesteatomas can erode the auditory ossicles and the walls of the antrum and extend into the middle cranial fossa.Īuditory ossicles, especially the long process and lenticular processes of the incus as well as the head of the stapes In more extensive disease erosions may be present. On CT a small cholesteatoma presents as a soft tissue mass. Scraps of cholesteatoma are visible in the external auditory canal. The ENT surgeon often states that cholesteatoma is a clinical diagnosis. Most cholesteatomas are acquired, but some are congenital. It gradually enlarges over time due to exfoliation and encapsulation of the tissue.
#2 mm enhancing nodule in internal auditory canal how to#
How to Differentiate Carotid Obstructions.TI-RADS - Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System.Esophagus II: Strictures, Acute syndromes, Neoplasms and Vascular impressions.Esophagus I: anatomy, rings, inflammation.Vascular Anomalies of Aorta, Pulmonary and Systemic vessels.Contrast-enhanced MRA of peripheral vessels.Ischemic and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy.Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System 2.0.Bi-RADS for Mammography and Ultrasound 2013.Transvaginal Ultrasound for Non-Gynaecological Conditions.Acute Abdomen in Gynaecology - Ultrasound.Appendicitis - Pitfalls in US and CT diagnosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
